Partes P Estudiar
1. Delante de cada complejo QRS hay una onda P (sólo una). 2. El intervalo PR es normal y constante. 3. La onda P es positiva en la derivación II y siempre igual. Frecuencia. La velocidad habitual de registro del papel del ECG es de 25 mm/seg, por lo tanto 1 mm (división pequeña) supone 0,04 seg y 5 mm (división grande) supone 0,20 seg.
ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS complex, ST segment, Twave

Intervalo PR: do início de P até o início do QRS. Duração normal: < 200ms (5 quadradinhos ou 1 quadradão).. (QTc) = QT medido / raiz quadrada de RR, usando os dois valores ou em segundos, ou QTc = QT medido / raiz quadrada de RR/1000, com ambos os valores em milissegundos. Para homens, QTc normais são aqueles com ≤ 440 ms;.
Complejo QRS

The normal T wave is usually in the same direction as the QRS except in the right precordial leads. In the normal ECG the T wave is always upright in leads I, II, V3-6, and always inverted in lead aVR. Normal ST segment elevation: this occurs in leads with large S waves (e.g., V1-3), and the normal configuration is concave upward.
Electrocardiograma ( ECG normal ) ( la onda P , Segmento PR , el intervalo PR, QRS , el

Keywords: Normal P axis; QRS axis; T axis; gender; age. Introduction. The use of ECG in making diagnosis of heart diseases is widely accepted in most communities. however, the presence of a very few number of Specialists and health care providers having limited idea on the use of ECG has made it necessary to point out this basic information. It.
La onda P refleja la despolarización de las aurículas. El complejo QRS corresponde a la

En general, podemos asumir que cada pico producido por el complejo QRS es un latido, por lo que será normal un ECG en el que a lo largo de un minuto se puedan contar entre 60 y 100 picos QRS. O lo que es lo mismo, entre 6 y 10 picos del complejo QRS cada 6 segundos. El ECG anterior es un ejemplo de una frecuencia cardíaca normal.
ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS complex, ST segment, Twave
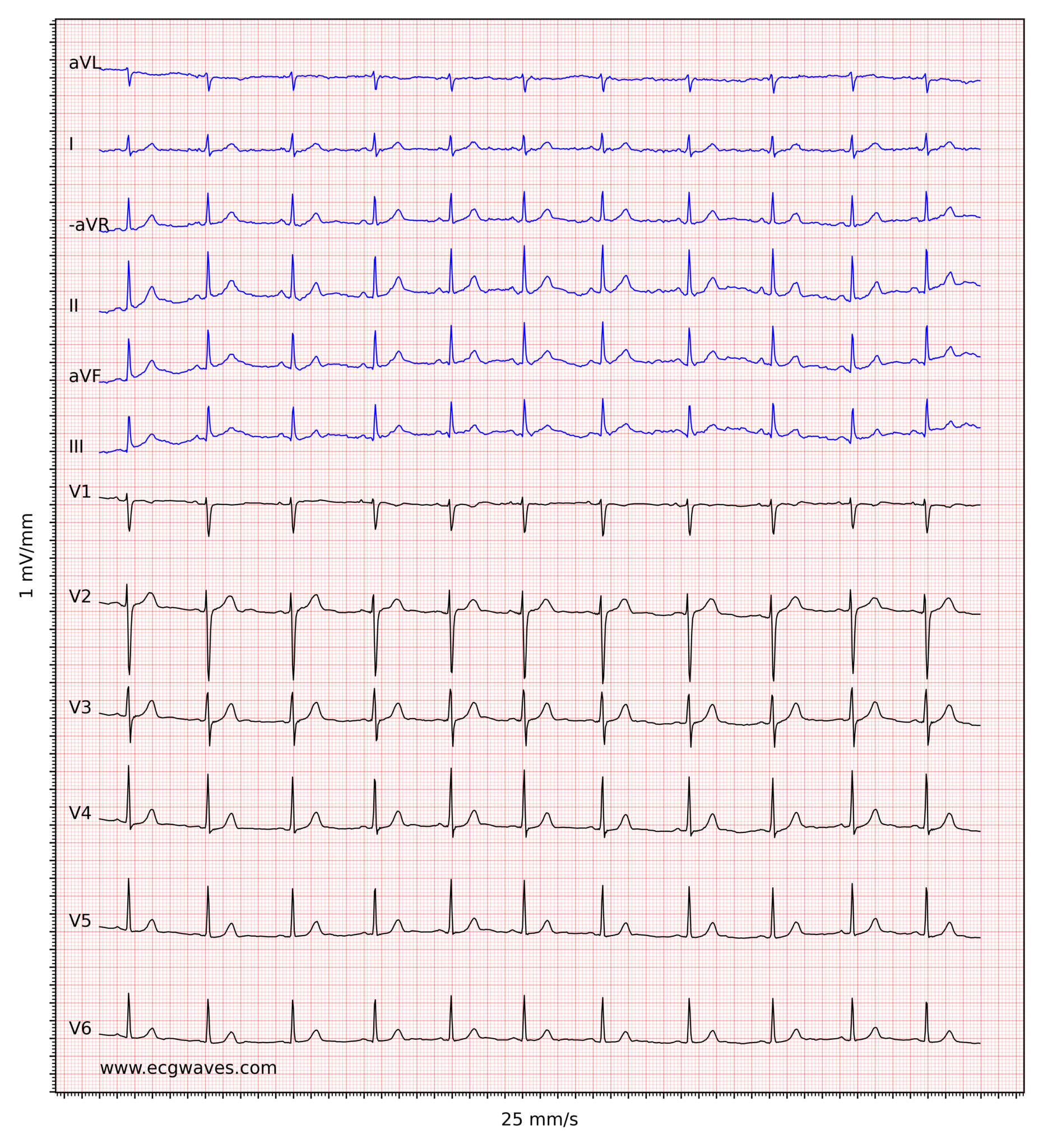
Common findings. Sinus rhythm (which is the normal rhythm) has the following characteristics: (1) heart rate 50-100 beats per minute; (2) P-wave precedes every QRS complex; (3) the P-wave is positive in lead II and (4) the PR interval is constant.; Causes of bradycardia: sinus bradycardia, sinoatrial block, sinoatrial arrest/inhibition, second-degree AV block, third-degree AV block.
QRS Interval on Your Watch ECG Narrow, Normal, and Wide Qaly

Los valores normales de la altura y duración de la onda son 2,5 mm y menos de 120 ms, respectivamente. -. El cálculo del eje de P (ÂP) se realiza de la misma forma que el del eje de QRS (ÂQRS). En condiciones normales (>90% casos) el ÂP oscila entre +30° y +70°. Nunca va más allá de +90° (P negativa en I ).
Traçado De Ecg Normal

El complejo QRS representa la despolarización ventricular. La onda Q es la deflexión descendente inicial y su duración normal es < 0,05 segundos en todas las derivaciones, excepto en V1-V3, en las cuales cualquier onda Q se considera anormal e indica un infarto de miocardio actual o pasado.. La onda R es la primera deflexión ascendente; no se definieron criterios absolutos para su altura.
ECG normal (15) Complejo QRS Dr. Alberto Sanagustín

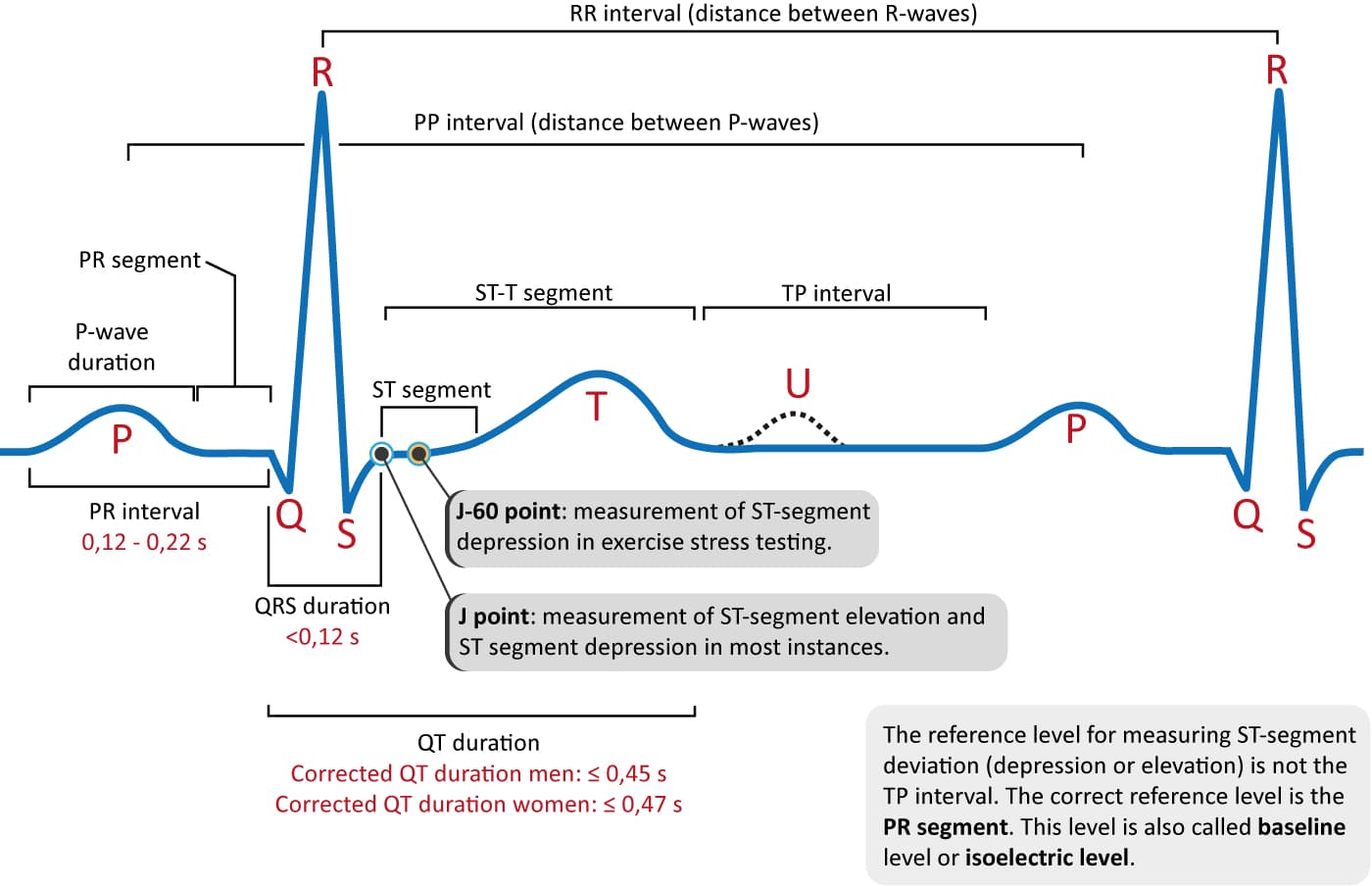
Se mide desde el comienzo de la onda Q o de la onda R hasta el final de la onda S (o R' si está es la última onda). Su valor normal está comprendido entre 0.06 s y 0.10 s. El intervalo QRS incluye al conjunto de ondas que conforman el complejo QRS, se encuentra alargado en los bloqueos de rama y en los síndromes de preexcitación. Intervalo QT
EKGInterpretation Merkmale des normalen EKGs (PWelle, QRSKomplex, STStrecke, TWelle) EKG

The QRS in Lead V6. The QRS complex is a set of waves that represents ventricular depolarization. Ventricular depolarization occurs in a rather complicated sequence (i.e. septal → free wall → basal wall depolarization). So, the appearance of the QRS complex tends to be more complicated than that of a p wave. The QRS complex can be thought.
PQRS Complex Nurse study notes, Pr interval, Nursing school motivation

QRS Duration; QT Interval; QRS Axis . Heart Rate. In normal sinus rhythm, a resting heart rate of below 60 bpm is called bradycardia and a rate of above 90 bpm is called tachycardia. PR Interval (measured from beginning of P to beginning of QRS in the frontal plane) Normal: 0.12 - 0.20s ; Short PR: < 0.12s Preexcitation syndromes:
PPT Interpretación clínica del ECG PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3814229
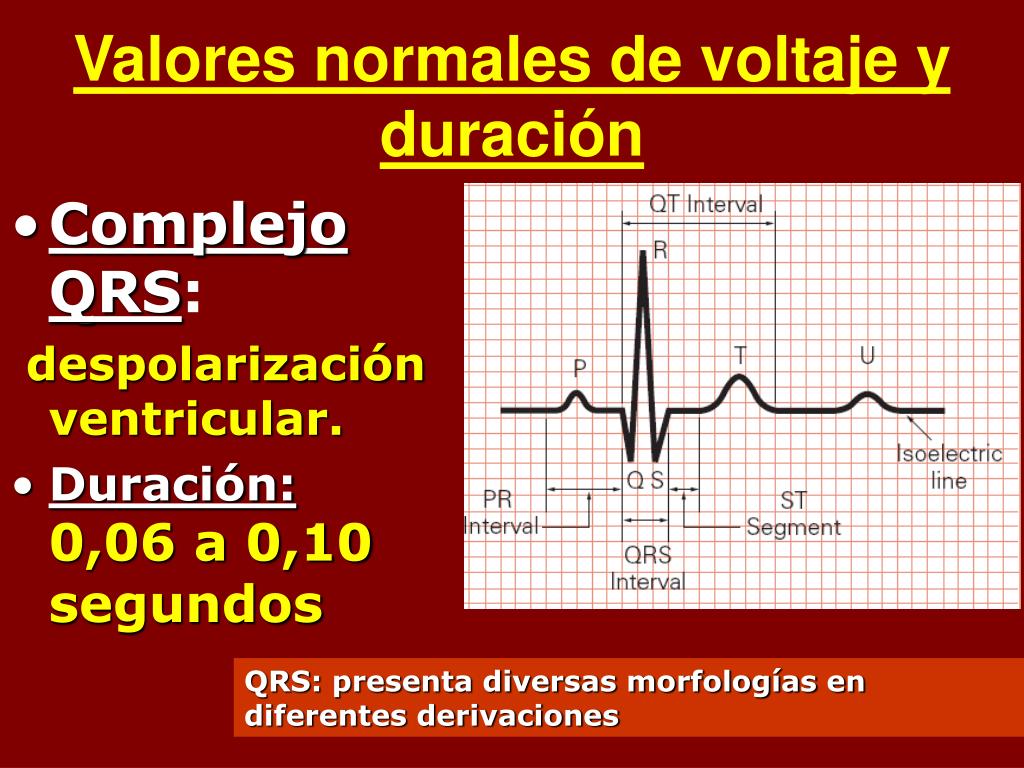
Ondas del Electrocardiograma. Publicidad. Las ondas son las distintas curvaturas que toma el trazado del EKG hacia arriba o hacia abajo. Son producto de los potenciales de acción que se producen durante la estimulación cardiaca y se repiten de un latido a otro, salvo alteraciones. Las ondas electrocardiográficas han sido denominadas P, Q, R.
The Cardiac Cycle on an EKG (PQRST Waves) YouTube

- Conocer y aprender a utilizar las tablas de valores normales.. Ritmo y eje de la onda P. 3. Eje del complejo QRS y de la onda T. 4. Onda P. 5. Complejo QRS. 6. Onda T y segmento ST. 7. Intervalos PR y QT. La figura 1 muestra los ajustes básicos del ECG, las ondas y los intervalos. 1. Frecuencia cardiaca
Electrocardiograma interpretación Electrocardiograma Ondas P, Q, R, S, T y U

The P-wave, PR interval and PR segment. ECG interpretation traditionally starts with an assessment of the P-wave. The P-wave reflects atrial depolarization (activation). The PR interval is the distance between the onset of the P-wave to the onset of the QRS complex. The PR interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles is normal.
ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS complex, ST segment, Twave
[Descárgate esta presentación] - ESTE es el VIDEO MAS COMPLETO, y además CON MUCHOS EJEMPLOS y EJERCIOS, PREGUNTAS DE EXAMEN, todo para que PUEDAS SEGUIR PRA.
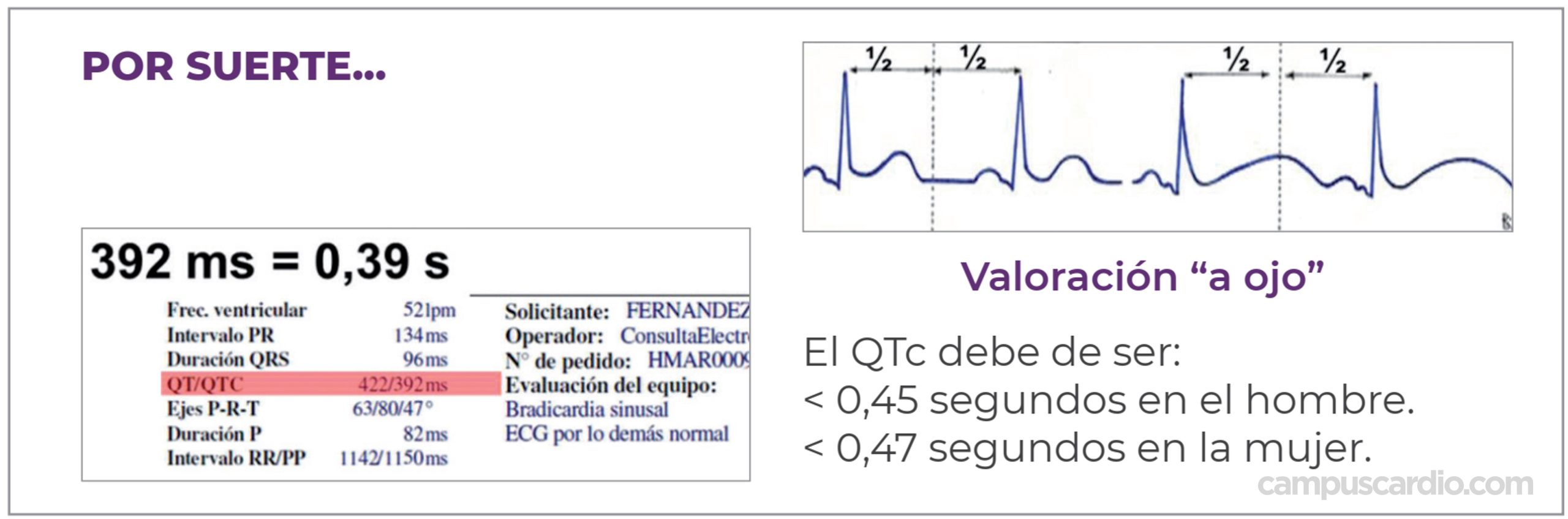
Análisis rápido del intervalo QT CampusCardio
P o - P-wave axis, QRS - QRS axis, T - T-wave axis, PR- PR- interval, QTc - QT corrected, msec - milliseconds, m- mean Figure 1: Scatter diagram of age and P wave axis. Figure 2: Scatter diagram of age and QRS axis.